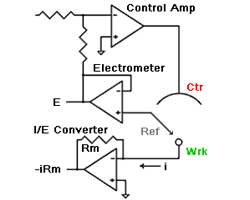
Potentiostat Architectures – Active I/E Converters
The Classical Potentiostat The schematic at the right is the classical potentiostat design shown in nearly every modern electrochemistry textbook. It has three basic features. The Working electrode is at Virtual Ground. The working electrode is at the same potential as the potentiostat’s electronic ground. This ground is often connected to Earth Ground. The electrometer Read more about Potentiostat Architectures – Active I/E Converters[…]