Potentiostat Fundamentals
Introduction
A potentiostat is an electronic instrument that controls the voltage difference between a Working Electrode and a Reference Electrode. Both electrodes are contained in an electrochemical cell. The potentiostat implements this control by injecting current into the cell through an Auxiliary or Counter electrode.
In almost all applications, the potentiostat measures the current flow between the Working and Counter electrodes. The controlled variable in a potentiostat is the cell potential and the measured variable is the cell current.

Prerequisites
This Application Note may be difficult to follow unless you have some familiarity with electrical terms such as voltage, current, resistance, frequency, and capacitance. If you feel your knowledge in this area is lacking, we suggest review of a very basic electronics or physics book.
Electrodes
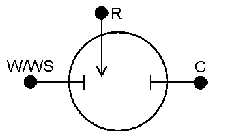
A potentiostat requires an electrochemical cell with three electrodes as shown below. W/WS denote the working and working sense. R denotes the reference electrode and C denotes the counter electrode.