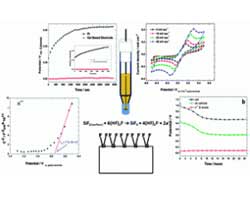
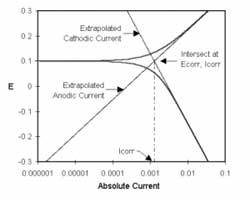
NSF Creates industry electrochemical research center at Ohio University
The Center for Electrochemical Engineering at Ohio Univ.’s Russ College of Engineering and Technology has received a National Science Foundation (NSF) award to establish a new industry university cooperative research center in Athens, Ohio, with partner site Washington University-St. Louis.
Led by Russ Professor of Chemical Engineering and Center for Electrochemical Engineering Director Gerri Botte, research at the new Center for Electrochemical Processes and Technology (CEProTECH) will focus on electrochemical alternatives to conventional chemical and biological processes, with the goal of enhancing advanced production capabilities, via a consortium model.
Consortium members will have access to pre-competitive, industry-driven research results and a dedicated 20,000-square-foot facility, located on Mill Street in Athens, Ohio, with more than $7 million in state-of-the-art equipment and infrastructure; students with specialized expertise in electrochemical engineering; and relationships with faculty, government labs and agencies, and other industry members.
[…]